Best Appendicitis Laparoscopic
Surgery in Delhi
Advanced Laparoscopic Surgeries
No cuts
Painless Surgeries
Affiliated to Best Hospitals in Delhi, NCR
Discharge in 24 Hours
Fixed price with no hidden cost
BEST APPENDICTICS TREATMENT IN DELHI
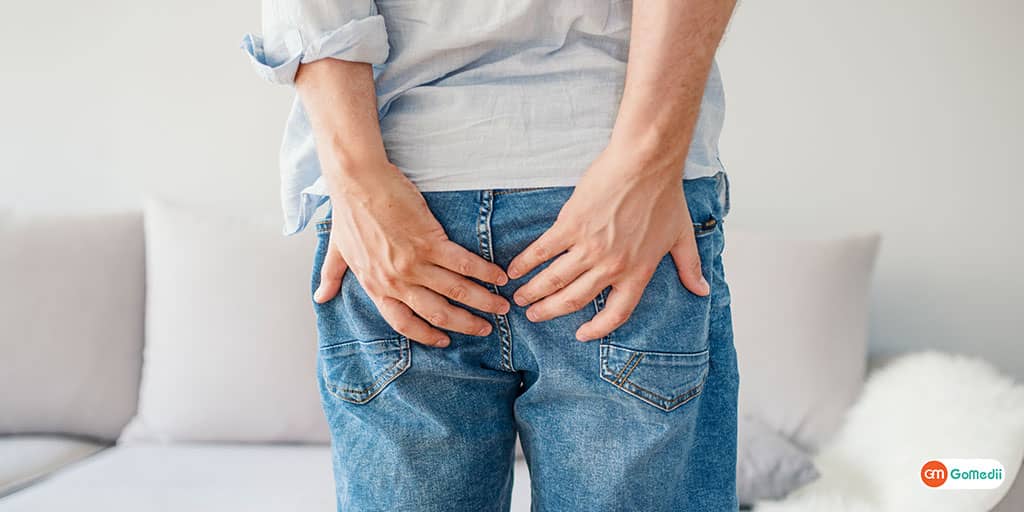
Acute appendicitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt diagnosis and management to prevent serious complications.
Dr Kapil Agrawal, one of the best appendicitis specialist in delhi, has handled complicated cases with excellent outcomes.
He has an overall experience of more than 22 years and has performed more than 2000 laparoscopic appendicectomies.
What is Appendicitis ?
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a small organ attached to the large intestine on the right lower side of the abdomen.
While its exact function remains unclear, when it becomes inflamed, it can lead to serious health issues.
Acute appendicitis is a common and urgent surgical condition. When it turns against you, the symptoms can be alarming.
If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications such as perforation, abscess formation, and peritonitis.
Symptoms of Appendicitis
The presentation of acute appendicitis can vary, but the classic symptoms include :-
→ Abdominal Pain: Acute appendicitis typically presents as vague abdominal pain that starts around the umbilical region and
later localizes to the right lower part of the abdomen. The pain is quite sharp and constant.
→ Nausea and Vomiting: Nausea and vomiting may occur after the onset of abdominal pain.
→ Anorexia: Loss of appetite is a common early symptom.
→ Fever: A low-grade fever may be present, but a high fever can indicate a more severe infection or complications like perforation.
→ Rebound Tenderness: Severe pain when the pressure in the right lower abdomen is suddenly released is a classical and diagnostic sign of acute appendicitis.
Complications of Acute Appendicitis
→ Perforation:A ruptured appendix can lead to peritonitis, a life-threatening infection of the abdominal cavity.
→ Abscess Formation: Localized collections of pus may form around the appendix, requiring drainage.
→ Sepsis: A severe, body-wide response to infection that can be fatal if not treated aggressively.
DIAGNOSIS OF APPENDICITIS
The diagnosis of acute appendicitis is primarily clinical but often supplemented by imaging and laboratory tests to confirm and assess the severity. Some of the common tests performed for the diagnosis include :-
Laboratory Tests
→ Complete Blood Count (CBC): Elevated white blood cell (WBC) count with a left shift (increased immature WBCs) suggests infection and inflammation.
→ C-reactive Protein (CRP): Elevated levels indicate inflammation.
Imaging Studies
→ Ultrasound: Often the first imaging modality used, especially in children and pregnant women. It can show a swollen appendix and free fluid.
→ Computed Tomography (CT) Scan:The gold standard for diagnosing appendicitis in adults. It provides detailed images showing an
enlarged appendix, fat stranding, and potential complications like abscess or perforation.
→ Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Used when radiation exposure needs to be minimized, such as in pregnant patients.
MANAGEMENT OF APPENDICITIS
The primary treatment for acute appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix (appendectomy). The approach to management may vary based on the severity and stage of appendicitis. The treatment protocol depends upon several factors :-
→ Duration of symptoms: The best time to operate this condition is within three days or 72 hours after the onset of symptoms.
→ Formation of appendicular lump: If the patient delays the treatment and radiological investigations show the formation of an appendicular lump, it’s better to plan
conservative management, and surgery is advised after 4-6 of treatment.
→ Development of complications: If the patient has started developing complications like the formation of abscess or pus, high-grade fever, or rupture of the appendix,
urgent surgical intervention is required as it can be life-threatening.
→ Condition of the patient: if the patient delays the treatment and the symptoms settle down, it’s better to postpone the surgery for 4-6 weeks.
This is known as Interval Appendicectomy.
BEST APPENDICITIS TREATMENT OPTIONS
Each patient's case presents unique challenges; therefore, personalized management approaches will ensure better health outcomes.
The choice of treatments often depends on individual circumstances such as age, overall health, and severity of symptoms.
Healthcare providers need to evaluate each case carefully before deciding on a management plan that best suits the patient’s needs.
NON-SURGICAL OR CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT
Under this plan, the surgeon administers antibiotics to combat infection. Patients are closely monitored for any changes in their condition.
If the symptoms improve, the surgery can be avoided for some time. However, the risk of recurrence remains higher compared to surgical management.
This treatment is mainly recommended in patients having mild symptoms or an uncomplicated appendicitis.
Patients having significant surgical risks in the form of medical diseases like uncontrolled diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart problems can also be advised for conservative management.
Patients presenting late in the hospital after 3-4 days of onset of symptoms and had formation of appendicular lump may be advised to defer surgery for a particular period.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT - Best Appendicitis Surgeon in Delhi
Surgical management of appendicitis typically involves the removal of the inflamed appendix, a procedure known as an appendectomy,
which can be performed using either Open or Laparoscopic techniques.
The decision to perform open or laparoscopic appendicectomy depends upon the experience and expertise of the surgeon as well as the condition of the patient.
Patients having significant surgical risks in the form of medical diseases like uncontrolled diabetes, high blood pressure, or heart problems can also be advised for conservative management.
Open Appendicectomy
The procedure requires a larger incision in the lower right abdomen. The surgery is associated with increased morbidity,
delayed recovery, and increased risk of complications.
The surgery is usually reserved for patients unfit for general anesthesia and patients having a severe abdominal infection or sepsis.
Appendicitis Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic Appendicectomy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure for removing the appendix, has become the gold standard for the removal of the appendix.
The laparoscopic surgeon can access the abdominal cavity with remarkable precision by utilizing small incisions and guided by a high-definition camera known as a laparoscope.
This approach reduces postoperative pain and significantly shortens recovery times compared to traditional open surgery.
An experienced and expert surgeon can easily navigate complex anatomy while minimizing tissue trauma, which contributes to lower rates of complications and faster return to normal activities for patients.
T The success of the surgery entirely depends upon the experience and expertise of the surgeon.
T A highly skilled surgeon can easily handle even complicated cases using minimally invasive techniques.
ADVANTAGES OF
SINGLE PORT LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY
Speedy Recovery
Early and Easy Mobility
Discharge within 24 hours
Virtually Scarless Surgery
Minor tissue trauma and less post-operative pain
Low risk of infection
Less Dependence on pain relievers
Almost no chance of hernia
Best Laparoscopic Surgeon for Appendicitis : Dr. Kapil Agrawal
→ Highly experienced team: Your surgical team, led by Dr. Kapil Agrawal, comprises highly experienced and skilled professionals
who specialize in laparoscopic procedures, including appendicectomies.
→ Single port laparoscopic Appendicectomy: We offer single port laparoscopic appendicectomy, a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses only
one small incision. This advanced procedure results in less postoperative pain,
minimal scarring, and a faster recovery time compared to traditional multi-port laparoscopy.
→ Empanelled with state-of-the-art hospitals: Our services are provided in state-of-the-art hospitals equipped with the latest medical technology and facilities.
The hospitals are equipped with modern operating theatres, advanced diagnostic tools, and comprehensive care units,
ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of medical treatment.
→ Complete cashless insurance facilities available:Our hospitals are empanelled with a wide range of insurance providers, allowing patients
to avail themselves of treatments without upfront payments. Our dedicated insurance coordination team assists with all
necessary paperwork and approvals, ensuring a seamless and stress-free experience for patients and their families.
→ Zero percent EMI options:We provide zero percent EMI options for our patients. This flexible payment plan allows patients to pay for their treatments
in manageable monthly installments without zero percent interest.
Book an Appointment Now:
+(91) 9999456455, +(91) 9910024564
FAQ
Surgery is the best option for managing appendicitis as it permanently removes the source of infection. This eliminates the chances of recurrent attacks and significantly reduces the risk of complications such as perforation or bursting of the appendix.
The appendix is a small, tube-like structure attached to the large intestine. The appendix has no function in the body and is a vestigial organ. Sometimes, the appendix can get inflamed, and it becomes necessary to remove it.
One can lead a perfectly normal life without an appendix. Removing the appendix does not significantly impact overall health or digestive function, as its role in the body is not essential.
The duration of hospital stay after a laparoscopic appendicectomy is usually short, often ranging from one to two days. However, this can vary depending on the patient's overall health and recovery from the surgery.
An appendicular lump is a mass that forms in the right lower abdomen due to an inflamed appendix surrounded by adherent loops of bowel and omentum. It is a protective mechanism to localize the infection and prevent its spread. The surgery in such patients becomes riskier due to increased chances of bowel injury.
Interval appendicectomy refers to the surgical removal of the appendix performed several weeks after an initial episode of appendicitis. This is done in cases that have been managed non-operatively with antibiotics. This approach allows inflammation to subside before surgery, especially when an appendicular lump has already formed.